Static Forces describe things that are not moving. We generalize these to things that are moving with no net force. You are being asked to complete three tasks that use examples of no net force.
Task 1: Set up a diagram with a 500g mass and two spring scales. Change the angle between the strings to 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 degrees. For each trial, record the scale value on the left and the scale value on the right. To do this, each string must be approximately the same length. Record your data in the group form.
Task 2: Use a logger pro to record the net velocity and acceleration for three trials of a car. For the first trial, the car should stand still. For the second, the car should be given a sharp push. For the third, a constant velocity buggy should be used. In each of the graphs, identify where NO acceleration and where CHANGING acceleration is taking place. Calculate the CHANGING acceleration or the constant velocity for two places in each trial.
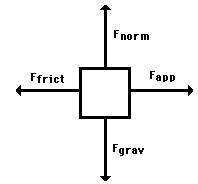
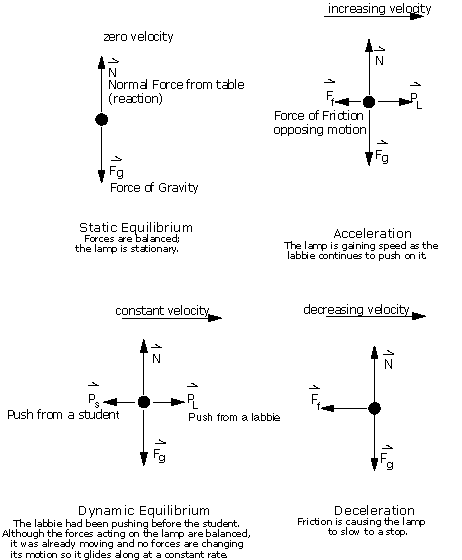
Task 3: Learn to use force diagrams as you work through ws1, ws2, and q1. There are some common conventions, shown in the pictures below.
Tuesday, October 25, 2011
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

No comments:
Post a Comment